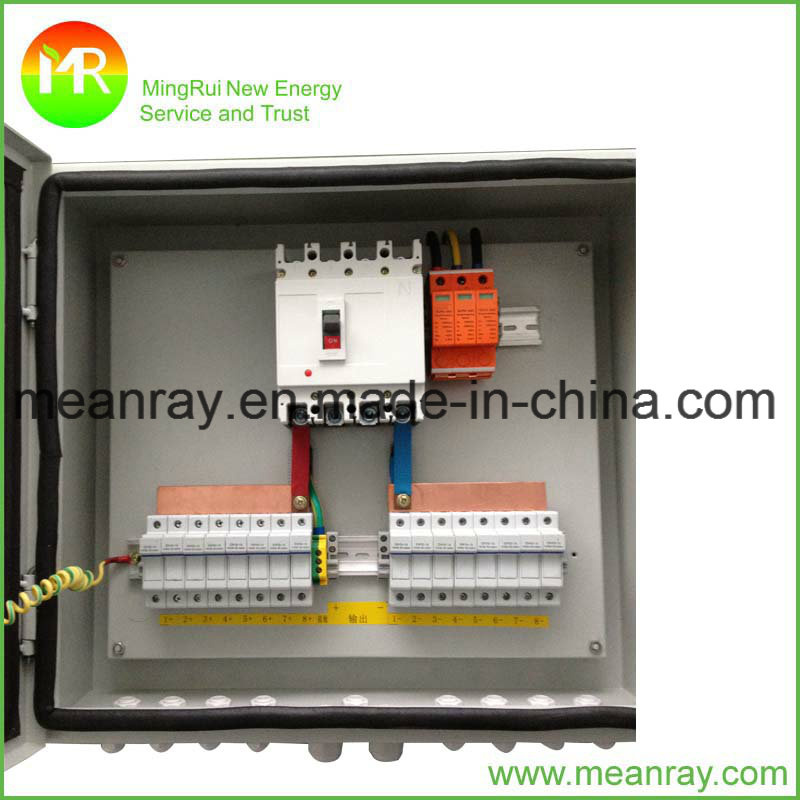
Fabulous Info About Are Junction Boxes Heat Resistant
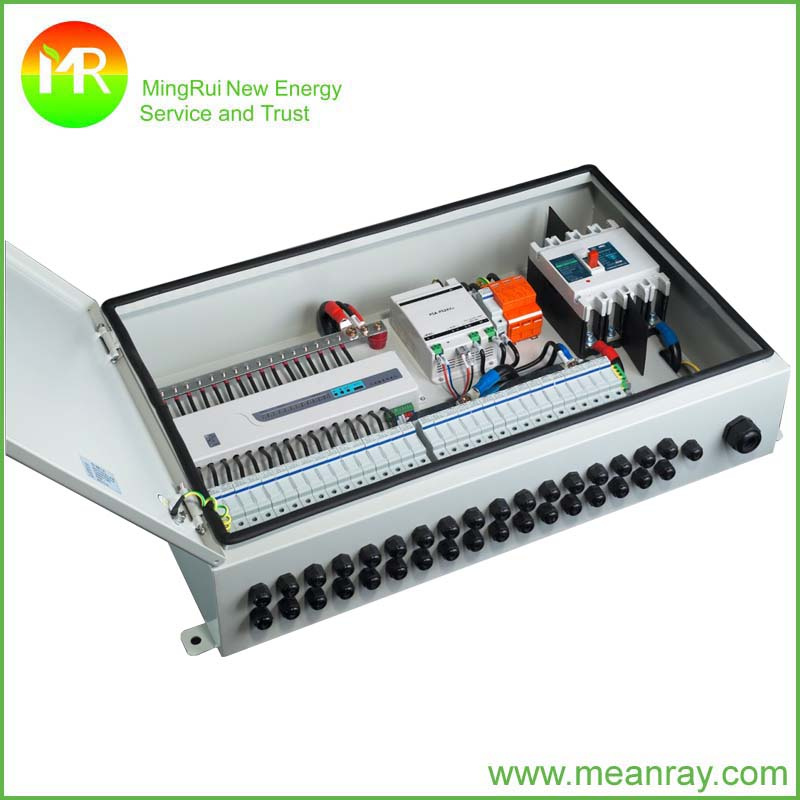

China Heat Resistant Junction Box Solar Array Combiner Details
Understanding Junction Boxes and Heat
Let's talk junction boxes. Those unassuming little enclosures are vital in electrical systems. They're the superheroes that keep your wire connections safe and organized, preventing shorts and potential fire hazards. But the question arises: are these little guys ready for a fiery challenge? Are junction boxes heat resistant? That's what we're diving into. After all, electricity generates heat, and we want to make sure our boxes can handle the pressure without melting into a sad, distorted mess.
The key here is material. Not all junction boxes are created equal. Some are made from plastic, others from metal. Think of it like comparing a lightweight t-shirt to a sturdy leather jacket — both serve a purpose, but they handle heat differently. Plastic boxes are generally less heat resistant than their metal counterparts. However, even plastic boxes have their limits and specific temperature ratings to consider. We'll break down the different types and their heat-handling capabilities.
And it's not just about the material itself. Installation practices play a significant role. Improper wiring can cause excessive heat buildup within the box, even if the box itself is rated for high temperatures. Think of it like trying to cram too much stuff into a suitcase — eventually, something's going to burst. Making sure you have proper connections and aren't overloading circuits is crucial for keeping things cool and safe.
So, before you start wiring up your next project, let's explore the world of junction boxes and heat resistance. We'll unravel the mysteries of temperature ratings, material choices, and best practices to ensure your electrical connections stay cool, calm, and collected. Get ready to ditch any electrical anxiety. You'll be practically an expert on these crucial electrical components.
1. Material Matters
Okay, let's get down to brass tacks. Or, perhaps more appropriately, copper wires. When discussing heat resistance, the material of your junction box is a major determinant. Plastic boxes, typically made from PVC or fiberglass, are common and affordable. They're great for many applications, but high heat isn't their forte.
PVC, while a decent insulator, can start to soften and deform at relatively low temperatures. Fiberglass offers better heat resistance than PVC, but it still has limitations. Always check the temperature rating on the box itself. This rating, usually expressed in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit, indicates the maximum temperature the box can withstand continuously without degrading. Exceeding this rating is like pushing your luck in a high-stakes poker game; eventually, you'll lose.
Metal junction boxes, typically made from steel or aluminum, are the heavy-duty champions of heat resistance. These boxes can handle significantly higher temperatures than their plastic counterparts. Think of them as the bodyguards of your electrical connections, standing strong against the heat. Metal also acts as a heat sink, dissipating heat away from the wires inside, further contributing to safety.
However, metal boxes have their own considerations. Grounding is critical. Since metal is conductive, proper grounding ensures that any fault current is safely directed back to the source, preventing shocks. Also, consider the environment. In corrosive environments, specialized coatings or stainless steel boxes may be necessary to prevent rust and degradation. Choosing the right material is like picking the right tool for the job — it makes all the difference.
304 Stainless Steel Explosionproof Box 300*400*200 Flameproof Type IIB
Temperature Ratings and Standards
Ever bought an appliance and seen a bunch of confusing symbols and numbers on the label? Temperature ratings on junction boxes can feel a bit like that. But don't worry, we're here to decode them. These ratings are essential because they tell you the maximum operating temperature the box can handle without failing. Ignoring them would be like ignoring the speed limit — you might get away with it for a while, but eventually, you'll run into trouble.
Common temperature ratings are usually expressed in degrees Celsius (C) or Fahrenheit (F). You might see markings like "Rated for 90C" or "Maximum Operating Temperature 194F." These numbers indicate the maximum continuous temperature the box can withstand. It's important to note that this is the ambient temperature inside the box, not necessarily the room temperature. Heat generated by the wires themselves can significantly increase the internal temperature.
Several standards organizations, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association), set guidelines and testing procedures for junction boxes. UL listing, for example, means that the box has been independently tested and meets specific safety requirements. NEMA ratings define the box's ability to withstand environmental conditions like water, dust, and corrosion. Looking for these certifications is like getting a stamp of approval from a trusted expert.
When selecting a junction box, choose one with a temperature rating that exceeds the expected operating temperature. It's always better to err on the side of caution. Consider the type of wires being used, the amount of current flowing through them, and the ambient temperature of the location. A little bit of planning goes a long way in preventing overheating and ensuring a safe and reliable electrical system. Think of it like planning a road trip — a little preparation can save you a lot of headaches down the road.
2. Installation Practices That Affect Heat
Okay, you've got your heat-resistant junction box. Great! But even the best box can fail if installed improperly. Proper installation is crucial for preventing excessive heat buildup and ensuring safety. Think of it like building a house — even the strongest materials won't hold up if the foundation is weak.
One common cause of overheating is loose connections. Loose connections increase resistance, which in turn generates heat. It's like trying to run a marathon with your shoelaces untied — you're going to struggle. Make sure all wire connections are tight and secure. Use the correct wire connectors and follow manufacturer's instructions carefully. Regular inspections and maintenance can help identify and correct loose connections before they become a problem.
Overloading circuits is another major culprit. Each circuit has a maximum current rating. Exceeding this rating causes the wires to overheat, which can then overheat the junction box. It's like trying to squeeze too much water through a small pipe — eventually, something's going to burst. Be sure to calculate the load on each circuit and avoid exceeding its capacity. Use appropriately sized breakers or fuses to protect against overcurrents.
Proper ventilation can also help dissipate heat. Avoid enclosing junction boxes in tightly sealed spaces where heat can accumulate. If possible, provide some airflow around the box. Consider using larger boxes to allow for better air circulation. Also, be mindful of the ambient temperature of the location. In hot environments, take extra precautions to prevent overheating. Think of it like choosing your clothing for the weather — dress appropriately to stay comfortable and safe.
Class 1 Division Junction Boxes Intrinsically Safe Store
Specific Applications and Considerations
Now that we've covered the basics, let's look at some specific scenarios where heat resistance is particularly important. Different applications have different requirements, and it's crucial to choose the right junction box for the job. It's like choosing the right vehicle for a road trip — a sports car might be fun, but it's not ideal for off-roading.
In high-temperature environments, such as near ovens, furnaces, or industrial machinery, heat-resistant junction boxes are a must. Use metal boxes with high temperature ratings and ensure that all wiring is also rated for high temperatures. Consider using ceramic wire connectors, which can withstand extreme heat. Regularly inspect the boxes and wiring for signs of degradation.
Outdoor applications also present unique challenges. Exposure to sunlight can increase the temperature inside the box, especially in dark-colored boxes. Choose boxes with UV protection to prevent degradation from sunlight. Also, consider the effects of rain and humidity. Use weatherproof or waterproof boxes to protect against moisture. NEMA ratings can help you select the appropriate box for the environment.
When dealing with high-current circuits, such as those used for electric vehicles or heavy machinery, heat is a major concern. Use metal boxes with adequate ventilation. Ensure that all wire connections are properly sized and tightened. Consider using heat sinks to dissipate heat away from the wires. Regularly monitor the temperature of the boxes and wiring to identify any potential problems.
Finally, consider the specific requirements of your local electrical codes. These codes often specify the type and size of junction boxes required for different applications. Compliance with these codes is essential for safety and legal reasons. Think of it like following the rules of the road — it keeps everyone safe.

So, Are Junction Boxes Heat Resistant? A Recap
The answer, as with many things in life, is "it depends." Junction boxes can be heat resistant, but it hinges on the material they're made from, their temperature rating, and how well they're installed. Ignoring these factors is like ignoring the warning signs on a carton of milk — you might regret it later.
Plastic boxes are generally less heat resistant than metal boxes, but even plastic boxes have specific temperature ratings. Always check the rating on the box and choose one that exceeds the expected operating temperature. Metal boxes, especially those made from steel or aluminum, can handle significantly higher temperatures. However, proper grounding is essential when using metal boxes.
Proper installation practices are crucial for preventing excessive heat buildup. Loose connections, overloaded circuits, and inadequate ventilation can all contribute to overheating. Make sure all wire connections are tight, avoid overloading circuits, and provide adequate ventilation around the box. Regular inspections and maintenance can help identify and correct potential problems before they become serious.
Ultimately, choosing the right junction box for the job is about understanding the application, considering the environment, and following best practices. A little bit of knowledge and a bit of caution can go a long way in ensuring a safe and reliable electrical system. And remember, when in doubt, consult a qualified electrician. It's always better to be safe than sorry.

Heat Resistant Junction Box Solar Array Combiner 6 String DC
